In the relentless race to the top of Google’s search results, content may be king, but technical SEO is the castle it lives in.
You can have the most engaging, well-researched content on the planet, but your ranking potential is dead in the water if search engine crawlers can’t find, understand, and index it efficiently.
Many businesses pour resources into content creation while overlooking the foundational cracks in their website’s technical health, leaving them wondering why their organic traffic is stagnant.
This in-depth guide will illuminate the most common and damaging technical SEO errors that could be silently hurting your website’s performance.
We’ll not only explore what these errors are and why they’re detrimental but also provide actionable steps on how to track and fix them using the latest information and best practices.
Why Technical SEO Matters?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing your website’s infrastructure to help search engines crawl and index your pages more effectively. A technically sound website provides a better user experience, which is a significant factor in how Google ranks content.
Think of it as building a house on a solid foundation. Without it, everything else you build on top is at risk of crumbling.
Technical SEO Errors to Track on Priority
1. Sluggish Page Speed and Poor Core Web Vitals
In our fast-paced digital world, patience is a virtue few possess. Slow-loading pages are a major deterrent for users and a confirmed ranking factor for Google. The introduction of Core Web Vitals has placed an even greater emphasis on user experience metrics.
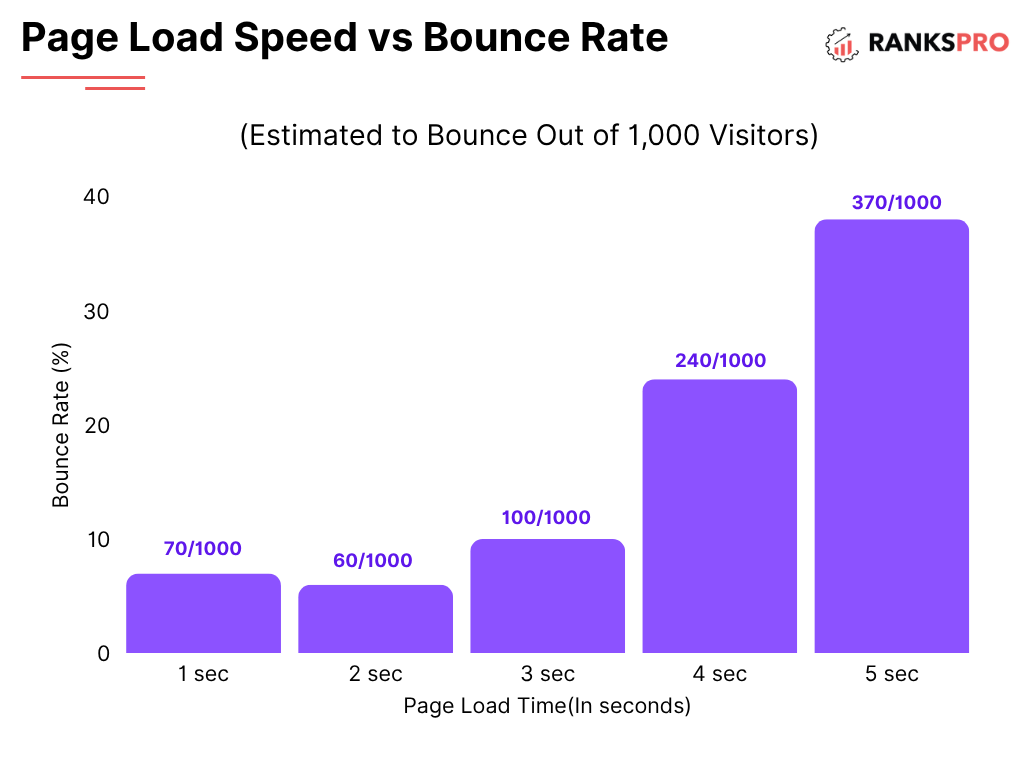
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- High Bounce Rates: Users are likely to leave a page that takes too long to load, signaling to Google that your page isn’t a good result.
- Poor User Experience: Slow and unstable pages frustrate users, leading to lower engagement.
- Direct Ranking Factor: Google’s Page Experience update incorporates Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS) into its ranking algorithm.
How to Track Them:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: This free tool from Google analyzes the content of a web page and generates suggestions to make that page faster. It provides both lab and field data on your Core Web Vitals.
- Google Search Console: The “Core Web Vitals” report in GSC shows you how your pages are performing based on real-world usage data.
- GTmetrix and Pingdom: These tools offer detailed performance reports, waterfall charts, and historical data to track your page speed over time.
Key Metrics to Watch:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. Aim for an LCP of 2.5 seconds or less.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures responsiveness. A good INP is 200 milliseconds or less.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Strive for a CLS score of 0.1 or less.
2. Mobile-Friendliness and Mobile-First Indexing Issues
With the majority of searches now happening on mobile devices, Google has shifted to mobile-first indexing. This means Google primarily uses the mobile version of your content for indexing and ranking. A poor mobile experience is no longer an option.
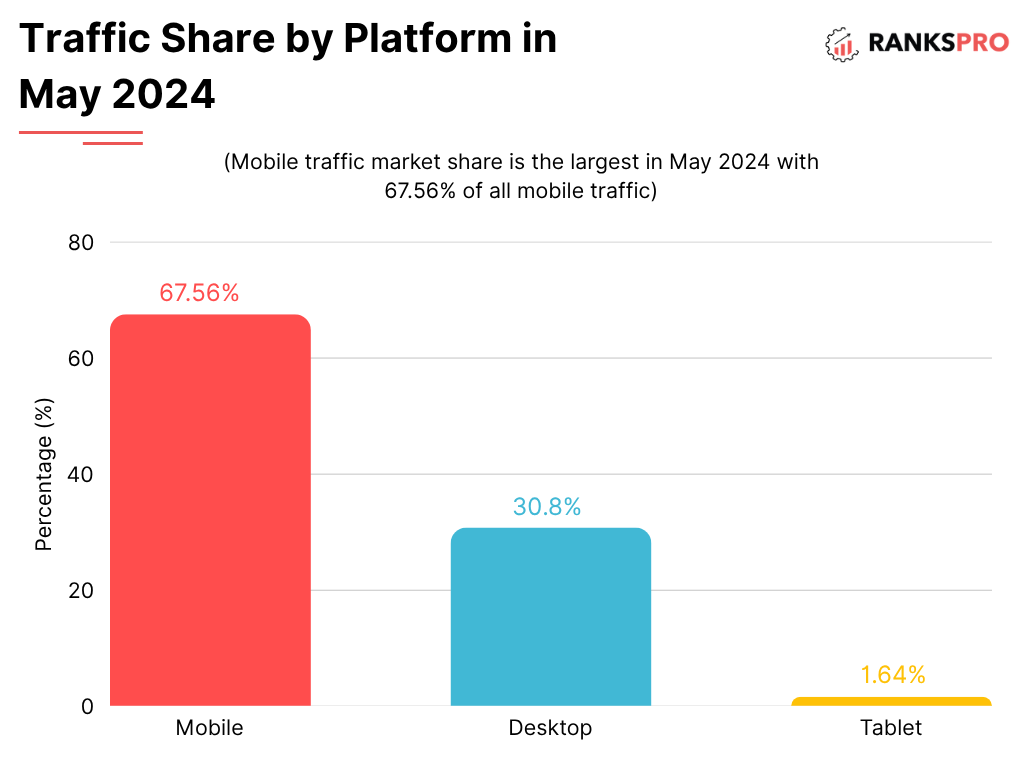
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Primary Indexing: If your mobile site is difficult to navigate or missing content that’s on your desktop site, it will directly impact your overall ranking.
- Negative User Signals: A non-responsive design on mobile leads to high bounce rates and low engagement.
How to Track Them:
- Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test: A quick and easy way to check if a page on your site is mobile-friendly.
- Google Search Console: The “Mobile Usability” report will identify any pages with mobile-friendliness issues.
3. Crawlability Errors and Wasted Crawl Budget
Search engines use bots (crawlers or spiders) to discover content on the web. If these bots can’t effectively crawl your website, your pages won’t get indexed and ranked.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Inaccessible Content: If important pages are blocked or hard for crawlers to find, they won’t appear in search results.
- Wasted Crawl Budget: Search engines allocate a “crawl budget” to each site. If this budget is wasted on unimportant or broken pages, your key content may be overlooked.
How to Track Them:
- Google Search Console: The “Coverage” report is your best friend here. It shows you which pages are indexed, which have warnings, and which are excluded, along with the reasons why.
- Review Your robots.txt File: Ensure you aren’t unintentionally blocking important pages or resources.
4. Indexing Problems: The “Invisible Website” Syndrome
Crawling is just the first step. For your pages to appear in search results, they must be indexed. Several technical issues can prevent Google from indexing your valuable content.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Pages Don’t Appear in SERPs: If a page isn’t indexed, it simply won’t rank for any keywords.
- Diluted Ranking Signals: Issues like duplicate or thin content can confuse search engines about which page to rank.
How to Track Them:
- Google Search Console “URL Inspection Tool”: Enter a specific URL to see its current index status and test the live URL.
- “site:” Search Operator in Google: A simple “site:yourwebsite.com” search will show you which pages of your site are indexed. If a key page is missing, you have an indexing problem.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: Check for “noindex” tags in the “Directives” tab.
5. Duplicate Content and Canonicalization Errors
Duplicate content exists when identical or “substantially similar” content appears on the internet in more than one place. This can happen both within your own site and across different domains.
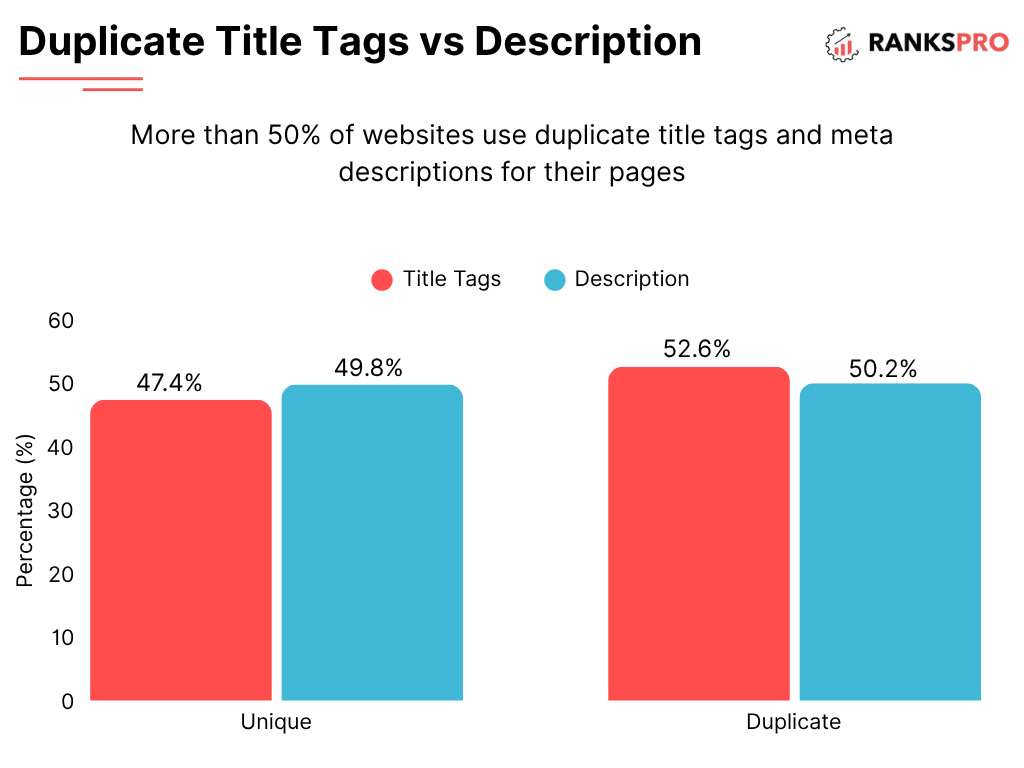
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Confuses Search Engines: Google may not know which version of the content to index and rank.
- Dilutes Link Equity: Backlinks may be split between multiple versions of the same page, reducing the ranking power of each.
How to Track Them:
- Siteliner: A free SEO tool that scans your website for duplicate content.
- Google Search: Use snippets of your text in quotation marks to see if it appears on other pages or websites.
With RanksPro’s SEO audit, you can easily discover these issues in one go:

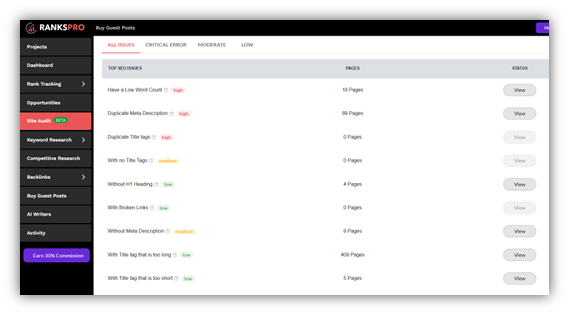
The Fix: Implement critical meta tags such as canonical tags (rel=”canonical”) to tell search engines which version of a page is the master copy that should be indexed.
6. Broken Links (Internal and External)
Broken links lead to a poor user experience and can hinder the flow of “link equity” (ranking power) throughout your site.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Poor User Experience: Clicking on a link that leads to a “404 Not Found” error page is frustrating for users.
- Wasted Crawl Budget: Crawlers may waste time on dead-end links.
- Diminished Link Equity: Broken internal links can prevent the flow of authority to other pages on your site.
How to Track Them:
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: The “Response Codes” tab will show you all the 4xx (client errors) and 5xx (server errors) on your site.
- Ahrefs’ Site Explorer: The “Broken backlinks” report shows you which external sites are linking to broken pages on your site.
- Google Search Console: The “Coverage” report will highlight 404 errors.
7. Improperly Implemented SSL/HTTPS
Security is paramount. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a confirmed, albeit lightweight, ranking signal. Not having it or implementing it incorrectly can cause issues.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Security Warnings: Browsers may display a “Not Secure” warning, which can deter visitors.
- Ranking Signal: Google gives a slight ranking boost to HTTPS websites.
- Mixed Content Issues: If your secure (HTTPS) page loads insecure (HTTP) content like images or scripts, it can create security vulnerabilities and display warnings.
How to Track Them:
- Check Your Browser’s Address Bar: Look for the padlock symbol next to your URL.
- Why No Padlock?: This online tool can quickly scan a page for mixed content issues.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: Crawl your site to find any remaining HTTP URLs that need to be redirected to their HTTPS counterparts.
8. Missing or Incorrect Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying its content. It helps search engines understand what your content is about, which can lead to rich snippets in the SERPs.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Missed Opportunity for Rich Snippets: Rich snippets (e.g., star ratings, FAQs, event information) can significantly improve your click-through rate from the search results.
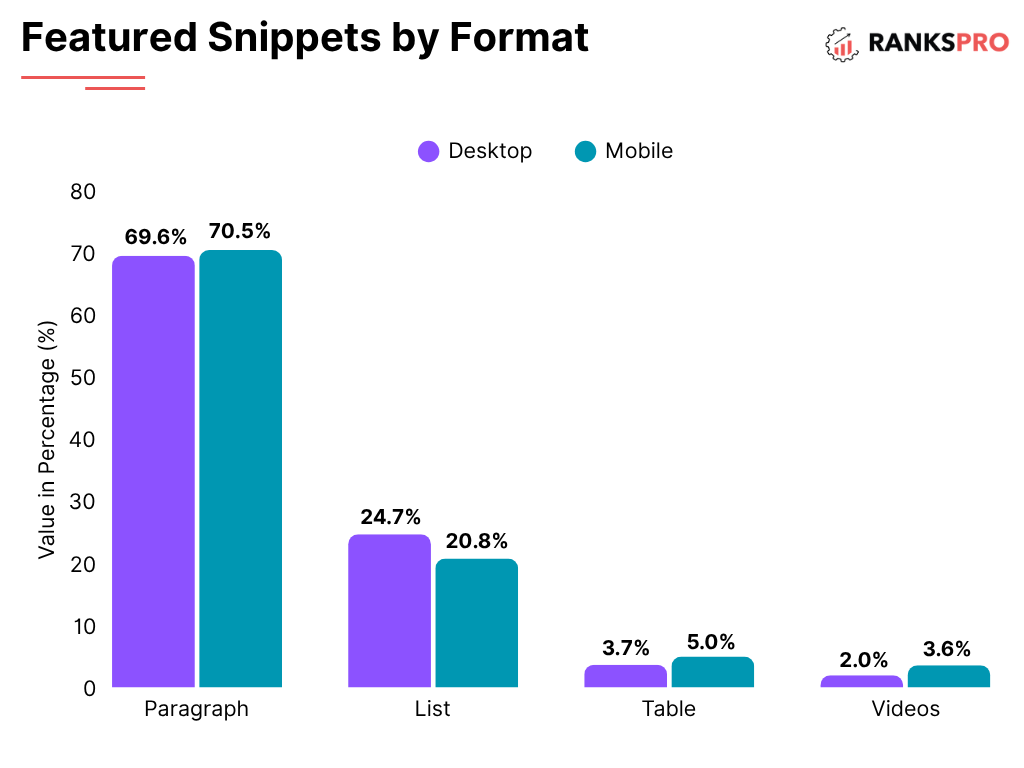
- Lack of Context for Search Engines: Without structured data, you’re not giving search engines the clearest possible information about your content.
How to Track Them:
- Google’s Rich Results Test: This tool allows you to test your structured data to see which rich results can be generated by your page.
- Schema Markup Validator: A more general-purpose tool for testing your schema markup.
- Google Search Console: The “Enhancements” section will show you which types of structured data Google has found on your site and whether there are any errors.
9. A Flawed XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a file that lists the important pages on your website, making it easier for search engines to find and crawl them.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Delayed Indexing of New Content: Without an up-to-date sitemap, it may take longer for search engines to discover your new or updated pages.
- Inclusion of Unimportant Pages: A bloated sitemap with non-canonical URLs, redirected pages, or low-quality content can waste crawl budget.
How to Track Them:
- Google Search Console: The “Sitemaps” report allows you to submit your sitemap and see if Google is able to process it correctly. It will also report any errors.
- Online XML Sitemap Validators: There are numerous free online tools that can check your sitemap for errors and formatting issues.
10. A Convoluted URL Structure
A clean, logical URL structure is beneficial for both users and search engines.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Poor User Experience: Short, descriptive URLs are easier for users to understand and share.
- Difficulty for Crawlers: A complex URL structure with many parameters and folders can make it harder for search engines to understand the hierarchy of your site.
Best Practices for URL Structure:
- Keep them short and simple.
- Use keywords where appropriate.
- Use hyphens to separate words.
- Maintain a consistent structure.
How to Track Them: A manual review of your URLs is often the best approach. You can also use a crawler to get a list of all your URLs for easy analysis.
11. Hreflang Horrors in International SEO
For websites with target audiences from multiple countries or languages, hreflang tags are crucial. They tell Google which language and regional version of a page to show to users.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Serving the Wrong Content: Users in one country may be shown the version of your site intended for another, leading to a poor user experience.
- Duplicate Content Issues: Without proper hreflang implementation, Google may see your different language versions as duplicate content.
12. The Plague of Thin Content
While not strictly a “technical” error in the same vein as a 404, pages with very little or low-value content can be flagged by Google and harm your site’s overall authority.
Why it Hurts Your Ranking:
- Doesn’t Satisfy User Intent: Thin content pages often fail to provide the information users are looking for.
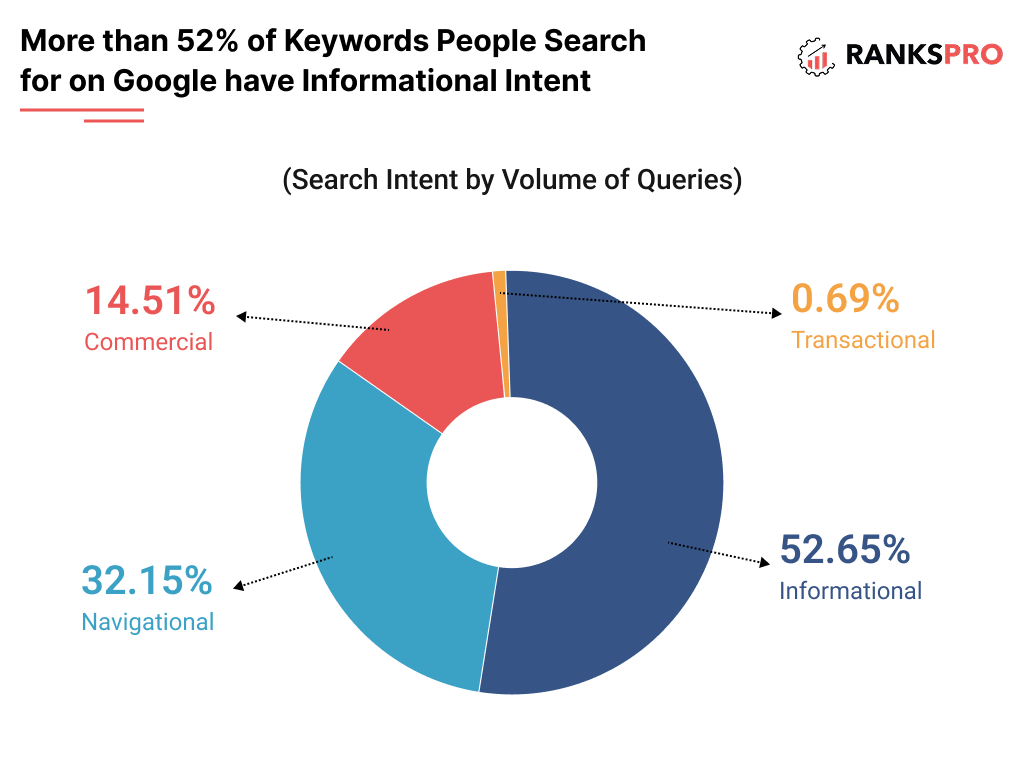
- Can Lower Your Site’s Overall Quality Score: A large number of thin content pages can signal to Google that your website is of low quality.
How to Track Them:
- Website Crawlers: Use a tool like Screaming Frog to identify pages with a low word count.
- Google Analytics: Look for pages with high bounce rates and low time on page.
Your Toolkit for a Technically Flawless Website
- Google Search Console: An essential free tool for monitoring your site’s health in the eyes of Google.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: The industry-standard tool for crawling websites and identifying a wide range of technical SEO issues.
- Google PageSpeed Insights: For in-depth analysis of your page speed and Core Web Vitals.
Conclusion: Make Technical SEO a Priority
Technical SEO is not a one-time fix. It requires regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure your website remains a welcoming place for both users and search engine crawlers.
By proactively identifying and addressing these common technical SEO errors, you’ll build a strong foundation that will support your content marketing efforts and propel your website to the top of the search engine rankings.
Start by conducting a thorough technical SEO audit with RanksPro today and unlock your website’s true organic potential.




