Backlinks are one of the most crucial ranking factors in SEO, helping websites gain authority, improve search rankings, and drive organic traffic. However, not all backlinks are beneficial—some can harm your website’s credibility and even lead to Google penalties.
With Google’s ever-evolving algorithms (such as Penguin and SpamBrain), low-quality, spammy, or manipulative backlinks can negatively impact your rankings instead of boosting them.
These toxic links can trigger manual actions, ranking drops, or even deindexing, making it essential for website owners to identify and remove harmful backlinks.
In this blog, we’ll explore the types of backlinks you should avoid to maintain a healthy, Google-friendly backlink profile. Understanding these bad backlink practices will help you protect your website’s SEO success and focus on earning high-quality, authoritative links that truly add value.
How Bad Backlinks Affect Search Rankings?
Backlinks have long been a cornerstone of SEO, acting as endorsements from other websites. However, not all backlinks are created equal. In fact, some can severely damage your website’s ranking and reputation.
This is primarily due to Google’s evolving algorithms and the penalties imposed on websites that engage in manipulative link-building practices.
Google’s Algorithm Updates & Penalties (Google Penguin, SpamBrain, etc.)
- Google Penguin
Introduced in 2012, Penguin targets websites with unnatural link profiles. It focuses on identifying and penalizing sites that use manipulative link-building techniques, such as buying links or participating in link schemes
Penguin’s emphasis is on the quality and relevance of backlinks, rather than sheer quantity. It aims to reward websites with natural, organic link profiles.
- SpamBrain
SpamBrain is Google’s AI-powered spam prevention system. It’s designed to identify and neutralize spammy links and other manipulative tactics. It is very good at detecting link schemes, and other forms of link manipulation.
- The Evolution of Link Evaluation
Google’s algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated in evaluating backlinks. They consider factors such as:
– Relevance: Links from websites that are relevant to your niche are valued more highly.
– Authority: Links from authoritative websites carry more weight.
– Naturalness: Links should appear natural and organic, rather than forced or artificial.
– Context: The surrounding content and the anchor text of the link are analyzed.
Google’s algorithms can detect unnatural link patterns and automatically demote websites in search results. A sudden drop in organic traffic is often a sign of an algorithmic penalty.
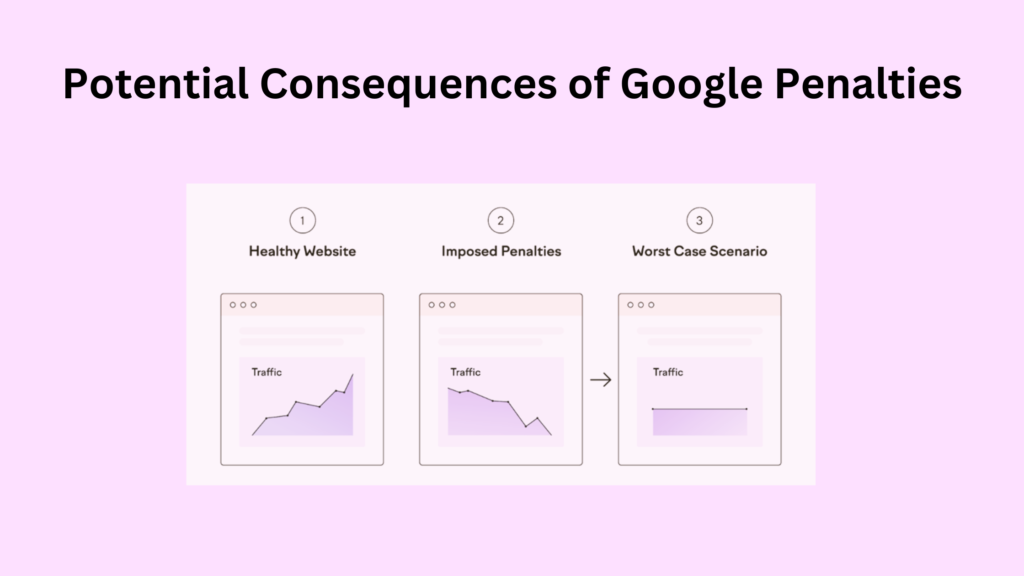
Loss of Trust and Credibility
Spammy links can damage your website’s reputation and erode user trust. Users who encounter spammy links may associate your website with low-quality or untrustworthy content.
Moreover, building spammy links is a waste of time and resources. It’s far more effective to focus on building high-quality, relevant backlinks through genuine content marketing and outreach.
Difficulty in Recovery and SEO
Recovering from a link related penalty can be a long and difficult process. It often involves manually disavowing spammy links and submitting a reconsideration request to Google.
Competitors may use negative SEO tactics, such as building spammy links to your website, to try to harm your rankings. It is important to monitor your backlink profile, and disavow any spammy links that you find.
By understanding the risks associated with spammy links and prioritizing ethical link-building practices, you can protect your website’s SEO and build a strong online presence.
Types of Backlinks You Should Avoid
Building a strong backlink profile is essential for SEO, but not all links are created equal. Some can severely harm your website’s rankings and reputation. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the types of backlinks you should avoid:
1. Private Blog Networks (PBNs)
PBNs are networks of privately owned websites designed specifically to manipulate search engine rankings. These networks often consist of expired domains with existing authority, purchased and repurposed to host low-quality or thin content and link back to the target site.
Google’s algorithms are now highly effective at detecting PBNs. They analyze patterns like shared hosting IPs, similar website templates, overlapping content, and unnatural link profiles.
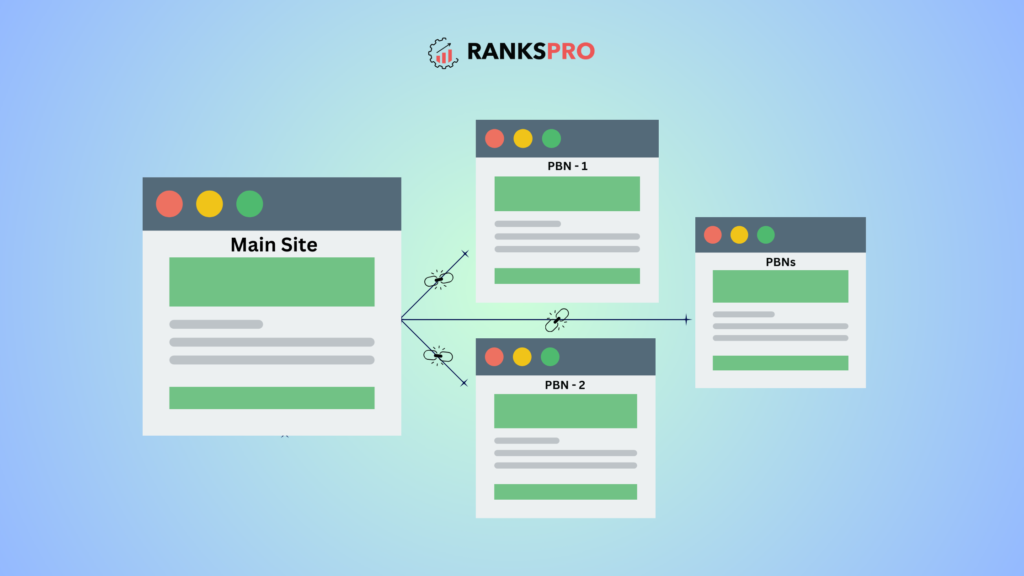
Key Indicators:
- Websites with generic or spun content.
- Unnatural linking patterns between network sites.
- Domains with no clear business purpose other than linking.
- Similar “whois” information.
2. Purchased Links
This involves directly paying for links, whether through link brokers, paid directories, or websites offering link placements. These links often lack editorial value and are solely intended to manipulate rankings.
Purchasing links violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and can result in manual penalties. Google’s algorithms are increasingly capable of identifying paid link schemes, even when disguised.
Key Indicators:
- Sudden spikes in backlinks from unrelated websites.
- Links with exact-match anchor text from low-quality sources.
- Offers for “guaranteed” rankings through link purchases.
- Websites that openly sell links.
3. Excessive Link Exchanges
This refers to reciprocal linking on a large scale, where websites agree to link to each other regardless of relevance. While some link exchanges are natural, excessive exchanges create unnatural link profiles.
Google favors natural, one-way external links. Excessive link exchanges can be seen as manipulative and can dilute the value of your backlinks.
Key Indicators:
- “Links” pages with numerous reciprocal links.
- Links from websites with no thematic connection to your own.
- A high ratio of incoming to outgoing links.
4. Links from Unrelated Niche Websites
These are backlinks from websites that have no topical relevance to your own site. For example, a website about cooking receiving links from a website about car repair.
Irrelevant links provide little value to users and can be seen as spammy. They can dilute the topical relevance of your website and confuse search engines.
Key Indicators:
- Websites with completely different topics and audiences.
- No overlap in content or keywords.
- Links that appear out of context.
5. Forum & Blog Comment Spam
This involves placing links in the comment sections of forums and blogs, often with irrelevant or spammy content.
Comment spam is a low-quality tactic that provides little value and can damage your website’s reputation. Most of these links are “nofollow,” meaning they don’t pass link equity.
Key Indicators:
- Generic or irrelevant comments.
- Keyword-rich anchor text.
- Links from low-quality forums and blogs.
6. Backlinks from Low-Quality Directories
These are links from directories that are spammy, outdated, or irrelevant. These directories often have poor design, excessive ads, and low-quality listings.
Low-quality directories provide little value and can damage your website’s reputation. Google prioritizes links from reputable and authoritative sources.
Key Indicators:
- Directories with poor design and usability.
- Excessive ads and spammy content.
- Low-quality listings and outdated information.
7. Footer & Sidebar Links from Random Websites
These are links placed in the footer or sidebar of unrelated websites, often as part of a link exchange or paid placement. These links are often seen as manipulative and provide little value. They can dilute the topical relevance of your website.
Key Indicators:
- Links in footers or sidebars of unrelated websites.
- Keyword-rich anchor text.
- Site wide links.
8. Links from Penalized or Deindexed Websites
These are backlinks from websites that have been penalized or deindexed by Google. Links from penalized websites can negatively impact your website’s rankings and associate it with spammy or manipulative practices.
Key Indicators:
- Websites that do not appear in Google’s search results.
- Websites with security warnings or malware.
- Websites that have been issued a manual action within google search console.
9. Auto-Generated & AI-Spam Backlinks
These are links generated automatically by software or AI tools, often with low-quality or irrelevant content. These links are easily detectable and can lead to penalties. They provide little value to users and can damage your website’s reputation.
Key Indicators:
- Irrelevant or nonsensical content.
- Keyword stuffing.
- Unnatural link patterns.
10. Site-Wide Links from Unrelated Domains
These are links that appear on every page of an unrelated website, typically in the footer or sidebar. Site-wide links are often seen as manipulative and provide little value. They can dilute the topical relevance of your website.
Key Indicators:
- Links that appear on every page of an unrelated website.
- Links with keyword-rich anchor text.
11. Backlinks from Hacked or Malicious Websites
These are links from websites that have been hacked or compromised, often without the website owner’s knowledge. These links can expose your website to security risks and damage your reputation.
Key Indicators:
- Websites with security warnings or malware.
- Sudden appearance of suspicious links.
12. Links from Gambling, Adult, or Drug-Related Sites
These are backlinks from websites that are associated with gambling, adult content, or illegal drugs. These links can damage your website’s reputation and associate it with harmful or inappropriate content.
Key Indicators:
- Websites with explicit or illegal content.
- Links that appear out of context.
13. No-Value Backlinks (That Waste Your Link Equity)
These are links that provide little or no value to users or search engines, such as links from low-quality directories or irrelevant websites. These links waste your time and resources and can dilute the overall quality of your backlink profile.
Key Indicators:
- Links from websites with low domain authority.
- Irrelevant content.
- Poor user experience.
14. Nofollow Links from Untrusted Sources
These are nofollow links from websites that are considered untrustworthy or spammy. While nofollow links don’t pass link equity, they can still associate your website with low-quality or untrustworthy sources.
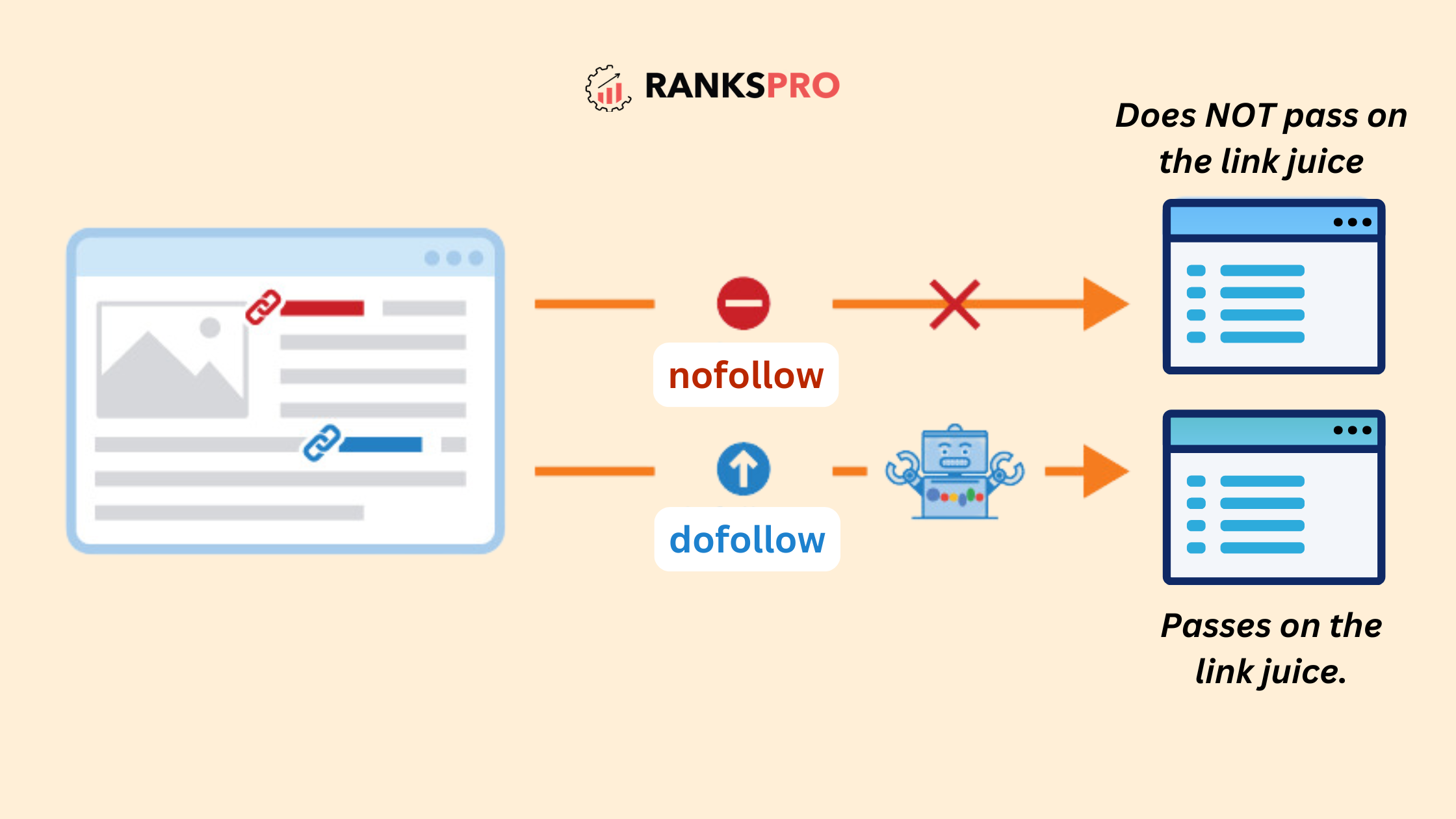
Key Indicators:
- Links with the “rel=nofollow” attribute.
- Links from websites with poor reputation.
15. Sponsored & Affiliate Links Without Proper Disclosure
These are sponsored or affiliate links that are not properly disclosed, violating Google’s guidelines and FTC regulations. Failure to disclose sponsored or affiliate links can lead to penalties and legal action.
Key Indicators:
- Links that appear to be endorsements or recommendations without proper disclosure.
- Lack of clear disclaimers.
How to Use RanksPro to Find Bad Backlinks?
Building a strong backlink profile is crucial for SEO success, but it’s equally important to identify and remove harmful backlinks that can negatively impact your rankings.
RanksPro’s Backlink Checker provides a comprehensive suite of tools to help you analyze your backlink profile and identify potentially damaging links.
Here are the steps to analyze your backlinks with RanksPro:
- Access the Backlink Checker: Navigate to the RanksPro platform and locate the “Backlink Checker” tool. Enter your website’s URL into the designated field and initiate the analysis.
- Analyze Your Backlink Profile: RanksPro will provide a detailed overview of your backlink profile, including:
- The total number of backlinks.
- Referring domains.
- Anchor text distribution.
- Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA) of referring domains.
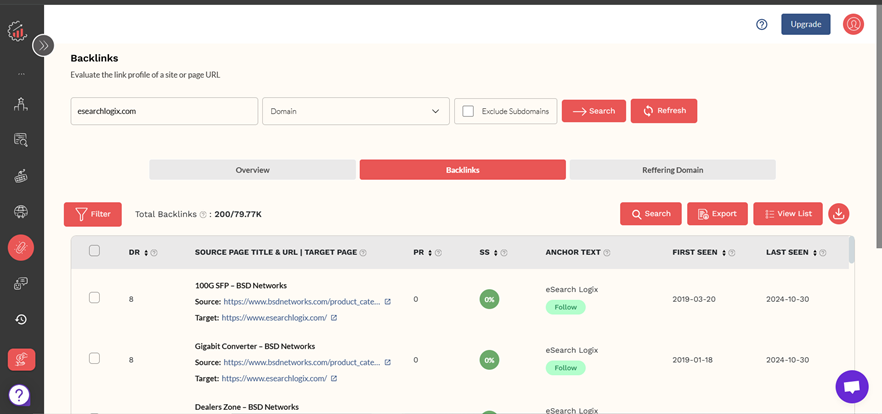
- Identify Low-Quality Referring Domains: Examine the list of referring domains and identify those with low DA and PA scores. Domains with extremely low authority are often indicators of spammy or low-quality websites.
- Analyze Anchor Text Distribution: Review the anchor text distribution to identify any unnatural patterns. Excessive use of exact-match anchor text can be a red flag, as it suggests manipulative link-building practices.

- Check for Irrelevant Referring Domains: Examine the websites linking to your site and determine if they are relevant to your niche. Links from unrelated websites can be a sign of spam or low-quality link-building.
- Identify Links from Penalized or Deindexed Websites: Use RanksPro to check the index status of referring domains. Links from websites that have been penalized or deindexed by Google can negatively impact your rankings.
- Detect Links from Suspicious or Malicious Websites: Look for links from websites with security warnings, malware, or inappropriate content. These links can damage your website’s reputation and expose it to security risks.
Benefits of Using RanksPro for Backlink Analysis
- Comprehensive Data: RanksPro provides a wealth of backlink data, allowing for in-depth analysis.
- User-Friendly Interface: The platform is easy to navigate, making it accessible to both beginners and experienced SEO professionals.
- Actionable Insights: RanksPro provides clear and actionable insights, empowering you to take control of your backlink profile.
- Time Efficiency: RanksPro automates the process of backlink analysis, saving you valuable time and resources.
- Regular Updates: RanksPro is regularly updated to reflect the latest algorithm changes and SEO best practices.
By using RanksPro’s Backlink Checker, you can effectively identify and remove bad backlinks, ensuring that your website’s SEO remains strong and healthy.




