The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Bard, and Llama has completely changed the way that users engage with information. For content creators and SEOs, this shift in the way users engage with information presents new challenges and unprecedented opportunities.
For those who want to succeed in this environment, it’s critical to understand how LLMs consume information and, even more significantly, how you can optimize your content to get it to effectively rank in them.
This comprehensive guide will examine approaches to source LLM ranking opportunities and apply them to claim that valuable top position and organic traffic!
The LLM Landscape: A New Frontier for SEO
SEO is no longer just about Google’s typical blue hyperlinks. LLMs are becoming the first stop for user queries, and often they will provide an immediate answer, summary, or synthesis of information.
This means that you are not just hoping someone clicks through to your website; you are looking for your content to be the source material for the LLM’s answer.
Key Shifts in User Behavior:
1. Direct Answers
Today’s users do not have the patience to endure slow, disjointed data. Rather than sifting through several search results, users expect a fast, easy, and accurate answer to the question. LLMs meet this expectation by providing one definitive answer at the beginning of an interaction.
This behavior continues to support the rise of “zero-click” searches, in which a user’s information needs are met without them clicking on a link.
According to a Semrush study, more than 13% of all Google search queries generated an AI Overview by the start of 2025. 43% of searches resulted in zero clicks – this was an even higher rate of zero clicks than for those with no AI Overview.
2. Conversational Queries
We are conducting searches more naturally and humanely. Users are moving away from short, keyword-based queries to longer, full-sentence questions because of the conversational nature of LLMs, which are designed to understand context and intent over multiple turns.

For example, instead of a simple search result of “best Italian restaurants in Milan,” the users may interact with a “large-language model [LLM]” with the full request “What are some affordable Italian restaurants in Milan, that are highly rated, and good for a first date?”
This shift in user behavior means understanding and responding to complex, multi-part requests will be a key function of a modern search.
3. Information Synthesis
Models like LLMs are great at pulling together information from a variety of locations and creating one singular answer. These models can read massive amounts of information and find ways to combine facts, statistics, and opinions to generate a coherent summary. Because of this ability, comprehensive and authoritative content is now more valuable than ever.
Research on LLM-driven traffic found that average website visitors from an LLM were 4.4% more likely to convert than an organic search visitor. They further found that although clicks may decrease, the traffic they are getting is considerably better quality.
Even if a user does not click through to a source that is cited or referenced by the LLM, authors can receive a different type of brand awareness.
To provide an example, suppose a travel blogger has an article about traveling to Japan on a budget data and LLM uses their article as the source for its response, even if the user never goes to the travel blogger’s site.
4. Reduced Click-Throughs
One outcome of these changes is the decline in click-through rates from websites. If an LLM provides a timely, satisfactory, and complete answer to a user’s inquiry, there is no need for the user to go to the source website.
This produces a paradox for content creators and marketers: their work may get seen or referenced more often by LLMs, but less often clicked through to on their websites.
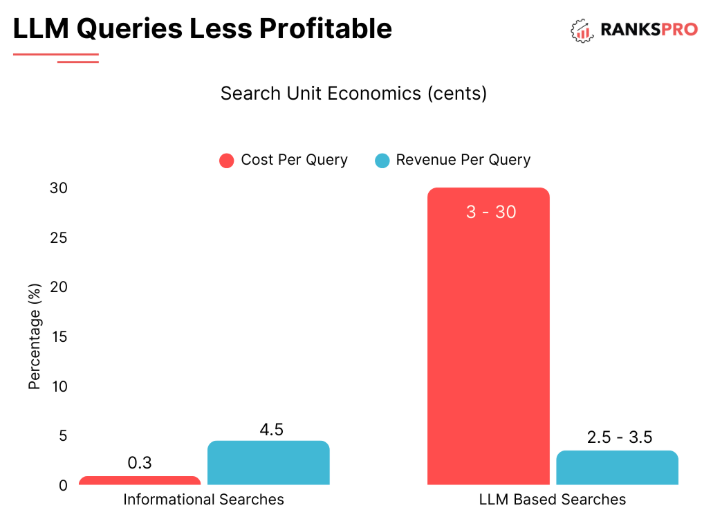
This trend, sometimes referred to as The Great Decoupling, indicates that impressions and clicks are more dissociated than what they used to be. Companies are beginning to consider metrics beyond clicks such as brand references, AI visibility, and brand perceptions within the LLM-generated outputs.
Understanding LLM Ranking Factors: Beyond Keywords
While there are still some important SEO considerations such as keywords, announcing links, and site speed; LLMs represent a new set of dimensions to ranking. LLMs rank by building out factual text and providing the human-like experience of relaying accurate, relevant, helpful information.
1. Contextual Relevance & Semantic Depth
LLMs are great at understanding context and language nuances. It’s not only about matching keywords. It’s about completely covering and analyzing a topic semantically.
- Topical Authority: You create content and keyword clusters of interconnected content and help Google understand that your website is an authority and trusted source on specific subjects.
- Entity Recognition: LLMs read the term “entities” (people, places, things, concepts). Establishing a firm definition for these entities and linking them in your subject-area content will add to your semantic coverage.
- Semantic SEO: Produce content that covers not only the key phrases used to search, but also the meaning and the intent behind the search. Get creative with synonyms, related phrases, and also use latent semantic indexing (LSI) keywords!
2. Accuracy & Factuality
LLMs have been trained on numerous data sources, but can still potentially “hallucinate” or share unsupported information. It is best to publish unique, verified content.
- Authoritative Sources: Cite authoritative sources and link to thousands of research studies.
- Data-Driven Content: Support claims with statistics, studies, and expert opinions.
- Updates: Keep your content newly written and accurate. This is particularly important in a fast-evolving area such as AI.
3. Clarity & Concise
LLMs are designed to extract and summarize information efficiently. Well-structured, easy-to-read content is more likely to be processed effectively.
- Scannability: Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, and short paragraphs.
- Active Voice: Write directly and avoid jargon where possible.
- “Answer Target” Content: Directly address common questions in your niche.
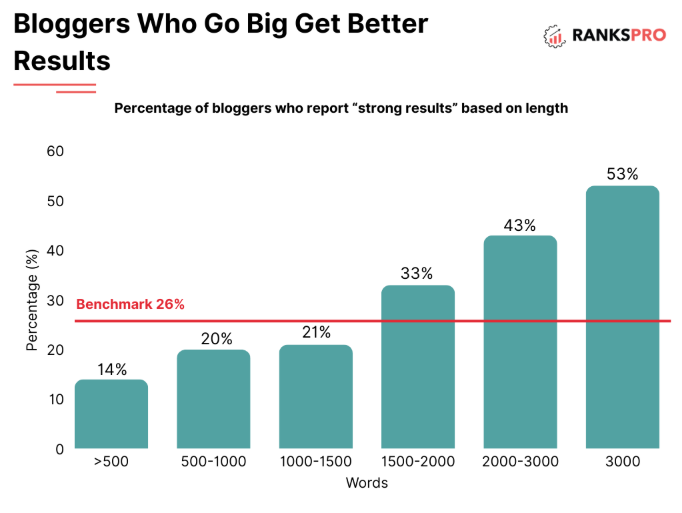
4. Completeness & Comprehensiveness
While conciseness is important for extraction purposes, completeness ensures your content answers the user’s query in full, a valuable reference point for an LLM to extract from.
- Depth of Coverage: Look across the many lenses of the topic area; ensure you consider every user intent (informational, commercial, navigational, transactional).
- FAQs & Q&A Sections: Address the questions that people are most likely to have related to your topic directly.
- Long-Form Content: Comprehensive guides (such as this!) can promote website authority and content length provides ample reference points for LLMs to synthesize.
5. User Engagement Signals (Indirectly)
Although LLMs do not include engagement metrics in the same way Google’s search algorithm does, the actual quality of content that generates good engagement (i.e., dwell time, low bounce) aligns with high quality the LLMs seek. High engagement is a sign the content is helpful and relevant to the user.
Tracking LLM Ranking Opportunities: Tools and Techniques
Finding LLM ranking opportunities requires both traditional SEO tools, as well as a newer analytical view.
1. Analyze Featured Snippets & People Also Ask (PAA) Boxes
These particular SERP features are strong indicators of what Google (and LLMs) is viewing as the best answer to a query.
Here are the tips to optimize for these features:
- Identify Queries: Look for keywords where your competitors rank for featured snippets or appear in PAA boxes.
- Study the Format: Analyze the structure (paragraph, list, table) of the featured snippet.
- Reverse Engineer: Create content that directly answers the PAA questions and is optimized for snippet-like formatting.
2. Monitor “Generative AI” Features in SERPs (e.g., SGE)
Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) directly demonstrates an LLM’s synthetization of information. It’s a good benchmark to consider when reviewing this model’s responses.
Here is the strategy to implement:
- Take Note of Sources: Whenever SGE provides an answer, see which websites it uses as sources. Strive to be one of those sources.
- Review Summaries: How does SGE summarize topics? Does it pull out specific points? Structure your content so SGE can summarize it as you designed it.
- Find Gaps: Are there questions SGE has issues with or no answer for? These are strong opportunities to create definitive content.
3. Keyword Research for Conversational Queries
Traditional keyword tools are evolving, but you can still adapt your approach.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Focus on longer and more natural language queries (e.g., “how do I integrate LLMs in to my marketing strategy,” instead of “LLM marketing”).
- Questions: Use tools to see the “who, what, where, when, why, how” questions that are related to your niche.
- Forum & Community Mining: Explore Reddit, Quora, and industry forums to understand the real questions users are asking.
- Google Search Console: Look at the searches you are already getting in to see if any of these are conversational, or question based.
4. Topical Gap Analysis
Where are the gaps in your existing content that LLMs might be looking to fill?
- Competitor Analysis: What topics do your competitors cover comprehensively that you don’t?
- Content Audits: Review your own content for outdated information or areas that lack depth.
- AI Content Audits: Use LLMs themselves! Ask an LLM to summarize a topic, then identify what information it didn’t include but would be valuable.
5. Sentiment Analysis
While less direct, understanding user sentiment around a topic can help you craft content that resonates and addresses concerns or desires.
- Tools: Social listening tools, sentiment analysis platforms.
- Strategy: Identify positive or negative sentiments associated with keywords or topics. Create content that reinforces positive aspects or addresses negative perceptions with solutions.
Implementing LLM Ranking Strategies: Actionable Steps
Once you’ve identified opportunities, it’s time to optimize your content.
1. Adopt a “Hub and Spoke” Content Model
A Hub and Spoke strategy is a content strategy that positions your website as an authority on a broad topic. The hub is one single, extensive “pillar page” that provides a comprehensive overview of a topic. A pillar page could have the title, “The Complete Guide to Artificial Intelligence.”
The hub page connects to “spoke” pages, which are individual articles that are more specific about sub-topics. Examples of spoke pages could include “The History of Neural Networks,” or “What is Machine Learning Algorithms.”
This hierarchy displays clear topic over topic, and informs LLMs that your website houses a considerable depth of organized knowledge on a topic, allowing you to become an excellent source for synthesis.
2. Prioritize Data-Driven and Fact-Checked Content
LLMs conveniently rank content that is credible and reliable. This means that in order to prove this you must substantiate your claims.
- Link to credible sources: Include hyperlinks to reputable third-party sources like academic research papers, industry studies, and even government reports. If you are writing about climate change, you might link to NASA report or study from a University.
- Use stats and numbers: Include relevant and current stats and numbers to add credibility to your content. A hypothetical example is, “70% of marketers are looking at using LLMs for content generation,” but you must find real stats that you can back up.
- Expert Interviews: Featuring quotes or insights from recognized subject matter experts adds a human layer of expertise and credibility. A quote from a leading data scientist in an article about LLM development can significantly boost its perceived authority
3. Optimize for Direct Answers and Snippets
LLMs are trained to provide concise, direct answers. To increase the likelihood that your content is used for these summaries, you must structure it for easy extraction.
- “In a Nutshell” Summaries: Start your articles with a brief, bolded summary (often called an executive summary) that directly answers the main question. For example, “In a nutshell, LLM ranking is the process of optimizing web content to be more easily discovered and synthesized by large language models.”
- Clear Headings and Subheadings: Use H2, H3, and H4 tags to break down content logically. This not only improves readability for humans but also provides a clear roadmap for LLMs to understand the content’s structure.
- Numbered and Bulleted Lists: Presenting information in a list format makes it highly scannable and easy for LLMs to parse and reuse. Think of these as perfect candidates for an AI-generated summary.
- Definitive Answers: Directly and explicitly answer common questions. Instead of hinting at an answer, state it clearly. For example, have a section titled “What is LLM ranking?” and provide a straightforward definition immediately.
4. Enhance Content for Semantic Understanding
LLMs have significantly more semantic and conceptual depth than traditional search engines.
- Optimizing for Entities: An “entity” is a defined idea, person, or place. When including key entities, e.g., “Generative AI” or “GPT-4,” be sure to boldface entities and link them to sources of authority, e.g., to Wikipedia or an official company page, etc. Doing so helps to build the contextual richness of your content.
- Maximizing Keyword Expression: Use different and varied related words instead of solely class-related words. Instead of using your main keyword “large language models” throughout, use sometimes “AI chatbots,” sometimes “generative AI,” and sometimes ” neural networks ” to show more understanding.
5. Improve E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines are crucial for traditional search, but they are even more so for LLMs. LLMs are trained on vast datasets, and they learn to recognize patterns of high-quality, trustworthy content.
- Author Bios: Include detailed author bios that highlight credentials, professional experience, and relevant affiliations. This proves the expertise behind the content.
- About Us Page: A transparent “About Us” page that clearly states your mission, team, and area of expertise builds trust with both users and LLMs.
- Security: Ensure your website uses HTTPS, which is a fundamental signal of trustworthiness and security.
6. Structure Content for Summarization
LLMs are fundamentally summarization machines. Your content should be structured to facilitate this process.
- Strong Introductions and Conclusions: Begin with a clear introduction that outlines the article’s purpose and end with a concise conclusion that summarizes the key takeaways.
- Topic Sentences: Start each paragraph with a strong topic sentence that encapsulates the paragraph’s main idea. This helps LLMs quickly grasp the content of each section.
- Internal Linking: Use internal links to guide LLMs and users through related content on your site. This reinforces the Hub and Spoke model and shows the depth and breadth of your content.
7. Monitor and Adapt
The LLM landscape is dynamic. What works today might need adjustment tomorrow.
- Regular Audits: Periodically review your content’s performance in LLM-driven searches.
- Analyze SERP Changes: Keep an eye on new generative AI features and how they present information.
- Feedback Loops: If possible, analyze user feedback on your content (e.g., comments, social shares) to gauge its helpfulness.
How RanksPro’s LLM Tracker Helps You Uncover Viable Opportunities?
The search landscape is evolving; people are no longer simply typing something into Google and clicking through results. People are now asking ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and other similar language models questions—and expecting answers immediately.
RanksPro’s LLM Rank Tracker is where becomes impactful.
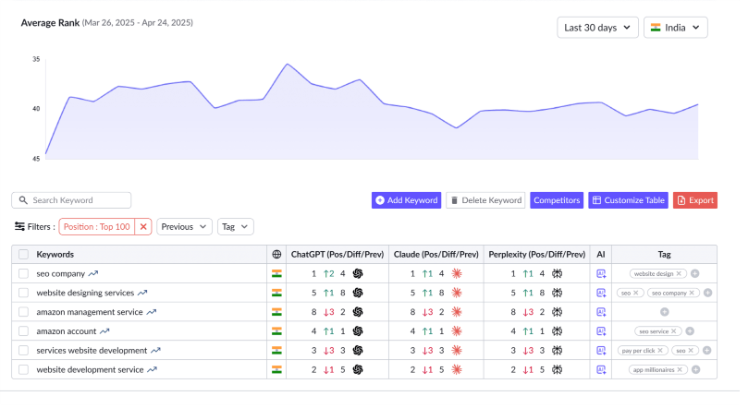
1. Track Exactly Which Prompts Attract Visibility
Think of knowing the exact prompts, whether they be a question or phrase, that generate responses from AI assistants that contain your brand. RanksPro tracks those prompts and provides you with:
- Where your site or brand is mentioned in ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity responses (i.e., number 1, 5 or not present at all)
- Your ranking progress or regression as a trend so you can monitor progress over time
- Your competitive ranking against other competitors on the same prompts.
2. Dive Deep with Rich Metrics
It’s not just a question of “are we being mentioned?” RanksPro provides you with the data used to strategize:
- Mentions: How often your brand is mentioned in AI-generated answers.
- Sentiment scores: Are those mentions positive, neutral, or negative?
- Visibility score: A composite score that quantifies where your brand sits overall in responses.
- Share of Voice (SOV): What portion of the AI answer landscape does your brand inhabit compared to competitors?
3. Keep an Eye on Shifting Trends in AI Visibility
LLMs are never static. RanksPro tracks your performance over time providing you:
- Changes in prompt performance – did a prompt drop big or rise big?
- Broken-down rankings – how often did you appear in the top 3 , top 10 or did not appear?
- New opportunities – you can see unranked prompts that you can pursue to grow.
4. Comparing Yourself with Competitors
You can identify which LLMs prefer your brand by using RanksPro’s Share of Voice dashboard.
- Determine the points at which your rivals are outperforming you.
- Track improvements or declines in visibility from week to week.
Putting briefly, RanksPro’s LLM Rank Tracker gives you the information you need to identify and seize laser-targeted chances in AI-driven discovery.
You can clearly see what works—and what hasn’t been published yet—instead of speculating about what might work in ChatGPT and other LLMs.




